Sun, Feb 22, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 26, Issue 118 (September & October 2018)
J Adv Med Biomed Res 2018, 26(118): 1-8 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mohaqeqi Kamal S H, Basakha M, Sajjadi H. The Prevalence and Risk factors of Limited Health Literacy in Iran: a Systematic Review and Meta-regression Analysis. J Adv Med Biomed Res 2018; 26 (118) :1-8
URL: http://journal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-4994-en.html
URL: http://journal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-4994-en.html
1- Dept.of Social Welfare Management, Faculty of Education Sciences and Social Welfare, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences,Tehran, Iran
2- Dept.of Social Welfare Management, Faculty of Education Sciences and Social Welfare, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences,Tehran, Iran ,basakha@gmail.com
2- Dept.of Social Welfare Management, Faculty of Education Sciences and Social Welfare, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences,Tehran, Iran ,
Abstract: (149634 Views)
There is a requisite need to document the health literacy status and its determinants for making recommendations for public health promotions. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of limited health literacy and its associated factors in Iranian studies. Search queries were made in PubMed, SCOPUS, SID, Irandoc, IranMedex, and Magiran from 2000 to 1 April 2016. The quality of the selected studies was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program checklists. Thirty one original papers were incorporated into the systematic review. We conducted meta-analysis using a random effects model. All analysis was performed using comprehensive meta-analysis [CMA] v.2 statistical software. The thirty one papers reviewed include data on 28,138 subjects, and report a prevalence of low health literacy between 4.8% and 79.9%. Pooled analysis of these data show that the weighted prevalence of low health literacy was 37.01% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 36.97%, 37.04%) and of marginal health, literacy was 30.76% (95% CI: 30.72%, 30.79%). Low educational levels, old age, poor employment situation, and low economic status were the most important determinants of limited health literacy. In the multivariate meta-regression model, the years of the studies were significantly associated with health literacy prevalence rates. Only a third of the population had adequate health literacy and health literacy was poor among vulnerable groups such as the unemployed, older and less educated people. So, considering appropriate strategies for each of these groups could have a significant role in improving community health literacy.
Full-Text [PDF 369 kb]
(157789 Downloads)
| | Full-Text (HTML) (4093 Views)
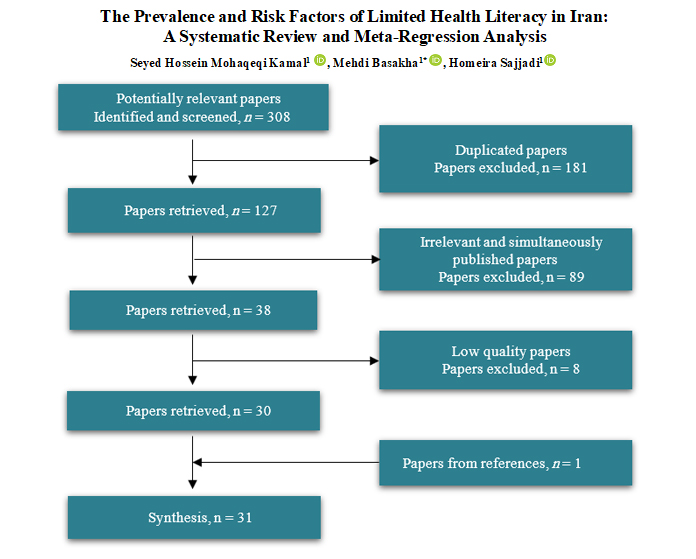

✅ Only a third of the population had adequate health literacy and health literacy was poor among vulnerable groups such as the unemployed, older and less educated people. So, considering appropriate strategies for each of these groups could have a significant role in improving community health literacy.
Type of Study: Review Article |
Subject:
Health Improvement Strategies
Received: 2018/01/10 | Accepted: 2018/07/30 | Published: 2018/08/1
Received: 2018/01/10 | Accepted: 2018/07/30 | Published: 2018/08/1
References
1. Nutbeam D, Kickbusch I. Advancing health literacy: a global challenge for the 21st century. Health promotion international. 2000;15(3):183-4.
https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/12.3.183 [DOI:10.1093/heapro/15.3.183]
2. Ratzan SC PR. Introduction. In: Selden CR ZM, Ratzan SC, Parker RM, editor. National Library of Medicine Current Bibliographies in Medicine: Health Literacy National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2000.
3. WHO, editor Health literacy and health behaviour. 7th Global Conference on Health Promotion: track themes; 2009; Kenya.
4. Kichbush I. translators: Sarmast H, Moosavian poor M. Health literacy and discussion on health and education Publication of Health Promotion and Healthy Lifestyle Association. 2006;2:4.
5. CSDH. Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health: final report of the commission on social determinants of health. 2008.
6. JCNHES. Achieving Health Literacy: An investment in the Future. Atlanta, Ga: Joint Committe on National Health Education Standards, American Cancer Society; 1995.
7. Baker DW, Gazmararian JA, Williams MV, Scott T, Parker RM, Green D, et al. Functional health literacy and the risk of hospital admission among Medicare managed care enrollees. American journal of public health. 2002;92(8):1278-83. [DOI:10.2105/AJPH.92.8.1278] [PMID] [PMCID]
8. Baker DW, Parker RM, Williams MV, Clark WS, Nurss J. The relationship of patient reading ability to self-reported health and use of health services. American journal of public health. 1997;87(6):1027-30. [DOI:10.2105/AJPH.87.6.1027] [PMID] [PMCID]
9. Javadzade H, Reisi M, Mostafavi F, Sharifirad G, Radjati F, Hasanzade A. Relationship between health literacy, health status, and healthy behaviors among older adults in Isfahan, Iran. Journal of Education and Health Promotion. 2012;1(1):31. [DOI:10.4103/2277-9531.100160] [PMID] [PMCID]
10. Scott TL, Gazmararian JA, Williams MV, Baker DW. Health literacy and preventive health care use among Medicare enrollees in a managed care organization. Medical care. 2002;40(5):395-404. [DOI:10.1097/00005650-200205000-00005] [PMID]
11. Schillinger D, Grumbach K, Piette J, Wang F, Osmond D, Daher C, et al. Association of health literacy with diabetes outcomes. JAMA. 2002;288(4):475-82. [DOI:10.1001/jama.288.4.475] [PMID]
12. Howard DH, Sentell T, Gazmararian JA. Impact of health literacy on socioeconomic and racial differences in health in an elderly population. Journal of general internal medicine. 2006;21(8):857-61. [DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00530.x] [PMID] [PMCID]
13. van der Heide I, Wang J, Droomers M, Spreeuwenberg P, Rademakers J, Uiters E. The Relationship Between Health, Education, and Health Literacy: Results From the Dutch Adult Literacy and Life Skills Survey. Journal of Health Communication. 2013;18(sup1):172-84. [DOI:10.1080/10810730.2013.825668] [PMID] [PMCID]
14. Adams RJ, Stocks NP, Wilson DH, Hill CL, Gravier S, Kickbusch I, et al. Health literacy: a new concept for general practice? Australian family physician. 2009;38(3):144.
15. CASP U. Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) 2014 Oxford: CASP Checklists; 2014 [
16. Khosravi A, Ahmadzadeh K, Arastoopoor S, Tahmasebi R. Assessing the Readability of Patient Education Materials about Diabetes Available in Shiraz Health Centers. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2014;14(8):661-7.
17. Tehrani S-A, Amirkhani MA. Health literacy and the influencing factors: a study in five provinces of Iran. 2007.
18. Ghanbari S, Majlessi F, Ghaffari M, Mahmoodi Majdabadi M. Evaluation of health literacy of pregnant women in urban health centers of Shahid Beheshti Medical University. Medical Daneshvar. 2012;19(97):1-12.
19. Khosravi A, Ahmadzadeh K. Investigating health literacy Level of patients referred to Bushehr hospitals and recognizing its effective factors. 2016.
20. Mohseni M, Khanjani N, Iranpour A, Tabe R, Borhaninejad V. Investigate the relationship between health literacy and health status among elderly people in Kerman-2013. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2015;10(2):0-.
21. Mollakhalili H, Papi A, Zare-Farashbandi F, Sharifirad G, HasanZadeh A. A survey on health literacy of inpatient's educational hospitals of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences in 2012. Journal of education and health promotion. 2014;3(1):66.
22. Peyman N, Samiee K. Investigating the status of health literacy among health providers of rural area. Journal of Health Literacy. 2016;1(1):46-52.
23. Tol A, Pourreza A, Rahimi Foroshani A, Tavassoli E. Assessing the effect of educational program based on small group on promoting knowledge and health literacy among women with type2 diabetes referring to selected hospitals affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013;19(104):10-9.
24. Malekzadeh S, Azami M, Mirzaei M, Motamedi F. Comparative Investigation of Health Literacy Level of Cardiovascular Patients Hospitalized in Private and Educational Hospitals of Kerman City, Iran. Acta Inform Med. 2016;24(1):56-60. [DOI:10.5455/aim.2016.24.56-60] [PMID] [PMCID]
25. Mohammadi Z, Banihashemi AT, Asgharifard H, Bahramian M, Baradaran HR, Khamseh ME. Health literacy and its influencing factors in Iranian diabetic patients. Medical journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran. 2015;29:230.
26. Nekoei-Moghadam M, Parva S, Amiresmaili M, Baneshi M. Health Literacy and Utilization of health Services in Kerman urban Area 2011. Tolue Behdasht Journal. 2012;11(14):123-34.
27. Seyedoshohadaee M, Barasteh S, Jalalinia F, Eghbali M, Nezami M. The relationship between health literacy and self-care behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Iranian Journal of Nursing Research. 2016;10(4):43-51.
28. Reisi M, Mostafavi F, Hasanzadeh A, Sharifirad G. The Relationship between Health Literacy, Health status and Healthy behaviors among Elderly in Isfahan. Health System Research. 2011;7(4):469-80.
29. Afshari M, Khazaei S, Bahrami M, Merati H. Investigating Adult Health Literacy in Tuyserkan City. Journal of Education And Community Health. 2014;1(2):48-55. [DOI:10.20286/jech-010248]
30. Haeri A TM, Rafieifar Sh, Soleimanian A, Sarbandi F, Ardestani M, Hashemi A and Montazeri A. The factor analysis of the urban population's health literacy. Payesh. 2016;15(3):251-7.
31. Haghighi ST, Lamyian M, Granpaye L. Assessment of the level of health literacy among fertile Iranian women with breast cancer. Electronic physician. 2015;7(6):1359.
32. Izadirad H, Zareban I. The Relationship of Health Literacy with Health status, Preventive Behaviors and Health services Utilization in Baluchistan, Iran. Journal of Education and Community Health. 2015;2(3):43-50. [DOI:10.20286/jech-02036]
33. Mahmoodi H, Negarandeh R, Javaheri M, Sharifi P, Ghanei R, AminPour A, et al. EXAMINING THE RELATION OF HEALTH LITERACY WITH OUTCOMES OF DIABETES AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETES PATIENTS IN SAQEZ, WESTERN IRAN, 2011. Journal of Urmia Nursing And Midwifery Faculty. 2014;12(1):56-62.
34. Rafizadeh Sh TB, Hassanjani S, Razavi M, Amjady M, and Hojjati H. . Relationship between the Health Literacy with self-efficacy of the diabetic patient's type 2referred to Gorgan city clinic in 2014. . Journal of Diabetes Nursing. 2014;3(2):30-42.
35. Tavoosi M HA, Rafieifar Sh, Soleimanian A, Sarbandi F, Ardestani M, Hashemi A and Montazeri A. Iranian Adult Health Literacy: A National Study. Payesh. 2016;15(1):95-102.
36. Javadzade H, Sharifirad G, Reisi M, Tavassoli E, Rajati F. Health Literacy among Adults of Isfahan. Iran J Health Syst Res. 2013;9(5):540-9.
37. Peyman N, Abdollahi M. The relationship between health literacy and self-efficacy physical activity in postpartum women. Journal of Health Literacy. 2016;1(1):5-12.
38. Qobadi M, Besharat M, Rostami R, Rahiminezhad A, Pourgholami M. Health literacy, negative emotional status, and self-care behaviors in dialysis. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health. 2015;17(1):46-51.
39. chehri mE, najafi mehri s, ebadi a, sarhangi f. Assessing the health literacy level of parents of preschool children. Iranian Journal of Pediatric Nursing. 2015;1(4):1-10.
40. Esna Ashari F, Pirdehghan A, Rajabi F, Sayarifard A, Ghadirian L, Rostami N, et al. The Study of Health Literacy of Staff about Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases in 2014. Scientific Journal of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. 2015;22(3):248-54.
41. Karimi S, Keyvanara M, Hosseini M, Jazi M, Khorasani E. The relationship between health literacy with health status and healthcare utilization in 18-64 years old people in Isfahan. Journal of Education and Health Promotion. 2014;3(1):75-.
42. Peyman N, Behzad F, Taghipour A, Esmaily H. Evaluation of communication between healthcare workers and patients with chronic diseases according to their levels of health literacy. Journal of Research & Health. 2014;4(1):599-607.
43. Shariatinia S, Fararoei M, Karimzadeh Shirazi K, Shams M. Assessment of HIV/AIDS literacy in 15-49 years old people in Yasuj and its related factors. Armaghane danesh. 2015;19(12):1082-95.
44. Azimi S, Ramezankhani A, Ghafari M, Rakhshani F, Ghanbari S. Comparison of health literacy between medical and non-medical students in Shahid Beheshti Universities in the academic year 92-93. Pajoohandeh Journal. 2015;20(2):78-85.
45. Reisi M, Mostafavi F, Javadzade SH, Mahaki B, Sharifirad G. Assessment of Some Predicting Factors of Self-efficacy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Iranian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2015;17(1):44-52. [DOI:10.5001/omj.2016.10] [PMID] [PMCID]
46. Paasche‐Orlow MK, Parker RM, Gazmararian JA, Nielsen‐Bohlman LT, Rudd RR. The prevalence of limited health literacy. Journal of general internal medicine. 2005;20(2):175-84. [DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.40245.x] [PMID] [PMCID]
47. Sahm LJ, Wolf MS, Curtis LM, McCarthy S. Prevalence of limited health literacy among Irish adults. Journal of health communication. 2012;17(sup3):100-8. [DOI:10.1080/10810730.2012.718041] [PMID]
48. Wu Y, Wang L, Cai Z, Bao L, Ai P, Ai Z. Prevalence and risk factors of low health literacy: A community-based study in Shanghai, China. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2017;14(6):628. [DOI:10.3390/ijerph14060628] [PMID] [PMCID]
49. Baker DW. The meaning and the measure of health literacy. Journal of general internal medicine. 2006;21(8):878-83. [DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00540.x] [PMID] [PMCID]
50. Nielsen-Bohlman L PA, Kindig DA. Health Literacy: A Prescription to End Confusion. Washington (DC): National Academies Press; 2004. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK216035.
51. Sun X, Shi Y, Zeng Q, Wang Y, Du W, Wei N, et al. Determinants of health literacy and health behavior regarding infectious respiratory diseases: a pathway model. BMC public health. 2013;13(1):1. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2458-13-261] [PMID] [PMCID]
52. Hoffman S, Marsiglia FF, Nevarez L, Porta M. Health Literacy among Youth in Guatemala City. Social Work in Public Health. 2016:1-8. [DOI:10.1080/19371918.2016.1188741] [PMID]
53. Hussein SH, Almajran A, Albatineh AN. Prevalence of health literacy and its correlates among patients with type II diabetes in Kuwait: A population based study. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2018;141:118-25. [DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2018.04.033] [PMID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |






